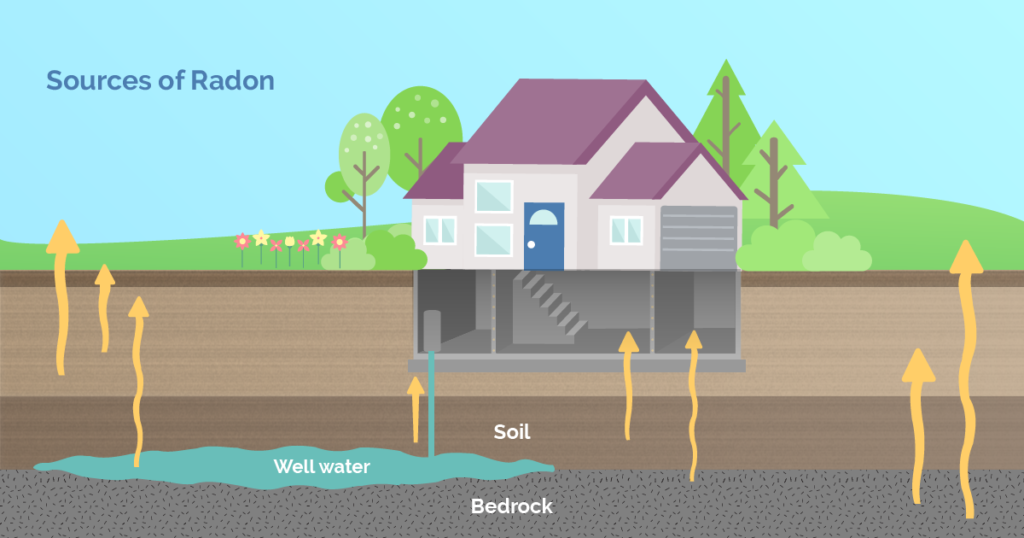
Radon, a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas, poses a significant health risk when it accumulates indoors, primarily in buildings. As a byproduct of the natural decay of uranium in soil and rock, radon can seep into homes and other structures through cracks in the foundation, gaps around pipes, and other openings. Commercial radon testing is crucial for assessing the levels of radon present in a building, as prolonged exposure to elevated levels of this radioactive gas can increase the risk of lung cancer. Various testing methods are employed, including short-term and long-term testing kits, continuous radon monitors, and passive devices. Short-term tests typically last from two to seven days, providing a snapshot of radon levels, while long-term tests extend for more than three months, offering a more comprehensive understanding of radon exposure over time. Once radon levels are determined to be above recommended thresholds, mitigation strategies are essential to reduce indoor concentrations and mitigate health risks. Radon mitigation techniques typically focus on preventing radon from entering a building or removing it once it has entered.
Active soil depressurization ASD systems are commonly employed, involving the installation of vent pipes and fans to draw radon from beneath the building and expel it outdoors, thus creating a negative pressure zone under the structure to prevent radon infiltration. Other mitigation approaches include sealing foundation cracks, clean vapor, improving ventilation, and installing radon-resistant features during new construction or major renovations. In commercial settings, radon mitigation strategies may vary based on the size and complexity of the building, how its specific structural characteristics. Large commercial buildings may require multiple mitigation systems to effectively address radon infiltration throughout the facility. Additionally, ongoing monitoring and maintenance are essential to ensure the continued effectiveness of mitigation measures and to verify that radon levels remain within acceptable limits over time. Building wellness initiatives increasingly emphasize the importance of indoor air quality, including the mitigation of radon gas.
Incorporating radon testing and mitigation into building wellness programs can contribute to healthier indoor environments, reduce the risk of occupant exposure to radon, and demonstrate a commitment to occupant health and safety. Moreover, addressing radon concerns proactively can help building owners and managers mitigate potential liability risks associated with radon exposure and ensure compliance with relevant regulations and guidelines. Commercial radon testing and mitigation strategies play a crucial role in ensuring indoor air quality and promoting building wellness. By implementing effective testing protocols, employing appropriate mitigation techniques, and prioritizing ongoing monitoring and maintenance, commercial building owners and managers can create safer and healthier environments for occupants while demonstrating a commitment to sustainability and occupant well-being. Integrating radon testing and mitigation into broader building wellness initiatives is essential for addressing this pervasive health risk and fostering a culture of health and safety in commercial buildings.
